Structure
A composite data type used to define a grouped list of variables, to be placed under one name in a block of memory is called structure. Thus, by using a single pointer to the structure, we can get access to different variables.
Syntax:
struct structure_name
{
data_type member1;
data_type member2;
.
.
data_type member;
};
Structure Advantages:
- Variables of different data types can be held by a structure.
- Objects containing different types of attributes can be created.
- The data layout can be reused across programs.
- Other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, etc., can also be implemented by a structure.
Structure Advantages Example :
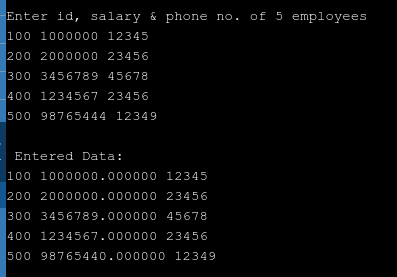
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main( ) { struct employee { int id; float salary; int phone; } ; struct employee e1,e2,e3,e4,e5; printf ("\nEnter id, salary & phone no. of 5 employees\n"); scanf ("%d %f %d", &e1.id, &e1.salary, &e1.phone); scanf ("%d %f %d", &e2.id, &e2.salary, &e2.phone); scanf ("%d %f %d", &e3.id, &e3.salary, &e3.phone); scanf ("%d %f %d", &e4.id, &e4.salary, &e4.phone); scanf ("%d %f %d", &e5.id, &e5.salary, &e5.phone); printf ("\n Entered Data: "); printf ("\n%d %f %d", e1.id, e1.salary, e1.phone); printf ("\n%d %f %d", e2.id, e2.salary, e2.phone); printf ("\n%d %f %d", e3.id, e3.salary, e3.phone); printf ("\n%d %f %d", e4.id, e4.salary, e4.phone); printf ("\n%d %f %d", e5.id, e5.salary, e5.phone); getch(); } |
Output: