XSLT Introduction
XSL stands for eXtensible Stylesheet Language. It is a styling language for XML. XSLT, on the other hand, stands for XSL Transformations and is used to transform XML documents into different formats, for example, transforming XML into HTML.
Example:
Books.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <bookstore> <book category="Child"> <title lang="en">ABC</title> <author>Author Name</author> <year>2020</year> <price>100.00</price> </book> <book category="IT"> <title lang="en">XQuery Book</title> <author>Author 1</author> <author>Author 2</author> <year>2005</year> <price>300.00</price> </book> </bookstore> |
XSLT Code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> <xsl:template match=""> <html> <body> <h2>List of Books</h2> <table border="1"> <tr bgcolor="#9acd32"> <th style="text-align:left">Title</th> <th style="text-align:left">Price</th> </tr> <xsl:for-each select="bookstore/book"> <tr> <td><xsl:value-of select="title"/></td> <td><xsl:value-of select="price"/></td> </tr> </xsl:for-each> </table> </body> </html> </xsl:template> </xsl:stylesheet> |
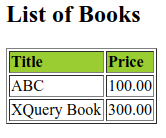
Output:
Prerequisites:
A basic understanding of HTML and XML.
XSLT Functions:
The same functions library is shared by XSLT 2.0, XPath 2.0, and XQuery 1.0. Thus, including over 100 built-in functions for string values, numeric values, date and time comparison, node and QName manipulation, sequence manipulation, and many more.