Reproductive System
- The cockroaches are dioecius (unisexual).
- They have well developed reproductive organs.
Male reproductive organ
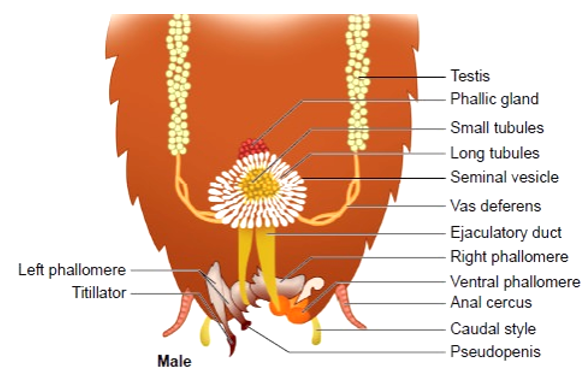
- Male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes. They are found on the lateral side of the body along the 4th -6th abdominal segments.
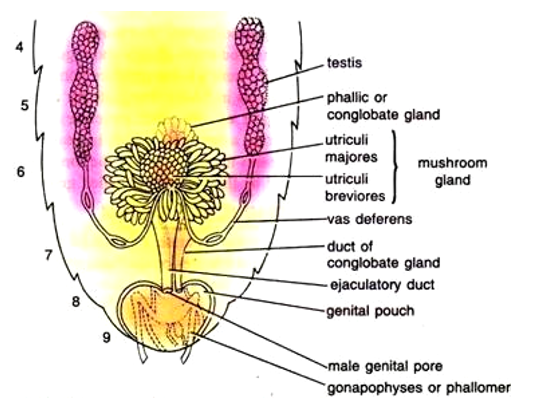
- A thin tube called vas deferens arises from the testis.
- Vas deferens opens into ejaculatory duct through seminal vesicle.
- The sperms are stored in the seminal vesicles and are glued together in the form of bundles called spermatophores which are discharged during copulation.
- The ejaculatory duct opens into male gonopore situated ventral to anus.
- The accessory gland is mushroom-shaped and it is present in the 6th-7th abdominal segments.
- The external genitalia are represented by male gonapophysis or phallomere (chitinous asymmetrical structures, surrounding the male gonopore).
Female reproductive organ
- The female reproductive system is composed of two large ovaries, present in the lateral side of the body along the 2nd – 6th abdominal segments.
- Each ovary is composed of a group of eight ovarian tubules (called ovarioles) which contain a chain of developing ova (or eggs).
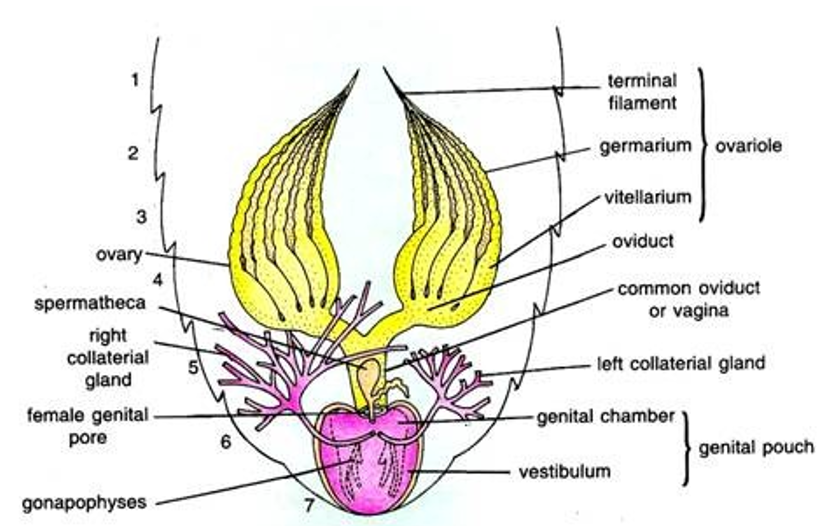
- Thin tubes called oviducts emerge from each ovary.
- Oviducts of each ovary unite into a single median oviduct (also called vagina) which opens into the genital chamber.
- A pair of spermatheca is present in the 6th segment which opens into the genital chamber.
Reproduction
- Sperms are released in bundles called spermatophores.
- These are transferred into the female genital chamber.
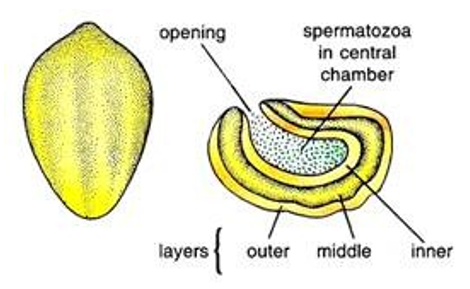
- The fertilised eggs are covered in hard capsules called oothecae.
- The color of Ootheca ranges from dark reddish to blackish brown. They are about 3/8″ (8 mm) long. They are dropped or glued to a suitable surface, usually in a crack or crevice of high relative humidity near a food source.
- Females produce nearly 9-10 oothecae at a time, each containing 14-16 eggs.
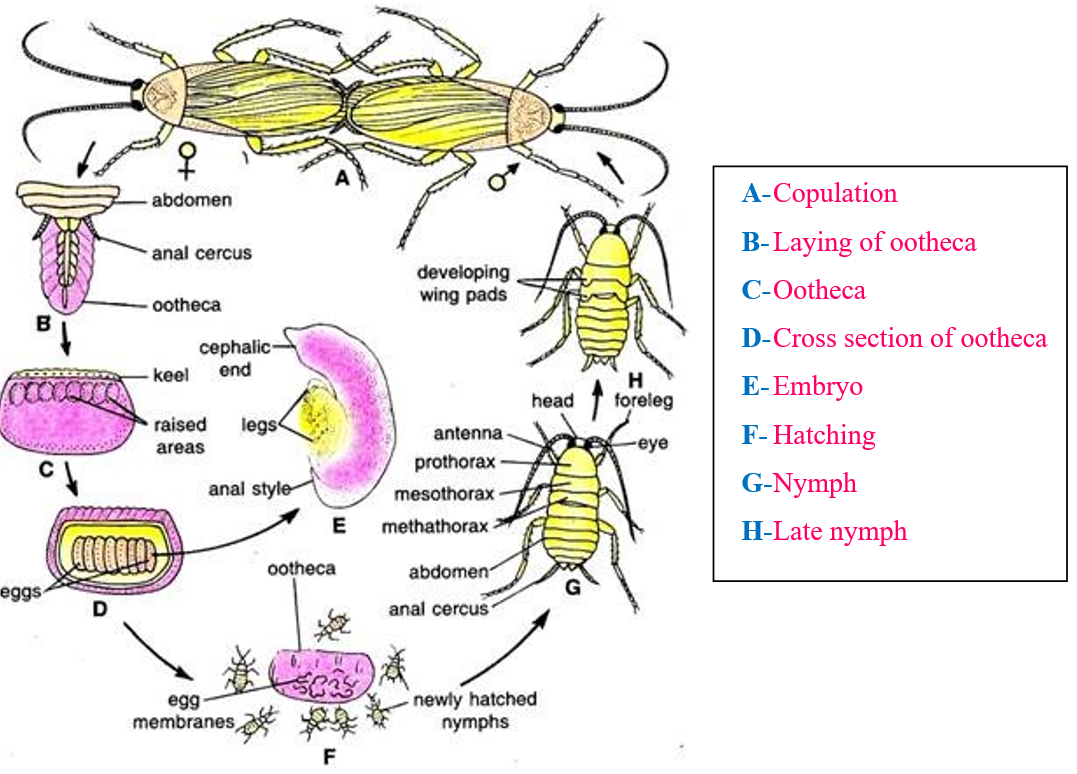
- Copulation
- Laying of ootheca
- Ootheca
- Cross section of ootheca
- Embryo
- Hatching
- Nymph
- Late nymph
Development
- The development of cockroach is indirect (or paurometabolous).
- Development involves a nymphal stage. The nymphs look very much like adults.
- There is metamorphosis. The nymph grows by moulting about 13 times to reach the adult form. Only the adult cockroaches have wings.