- The fruit is the mature or ripened ovary of a plant. Fruits enclose the seeds. The branch of horticulture that deals with the study of fruits and fruit cultivations is known as pomology.
- Fruit is developed from a fertilized ovary. If the fruits are developed without fertilization, it is called a parthenocarpic fruit, and the phenomenon is known as parthenocarpy. In some plants, some parts of the flower are also involved in fruit formation. Such a fruit is called a false fruit or pseudocarp.
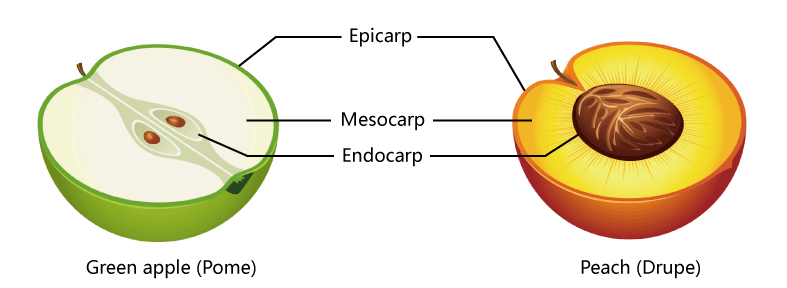
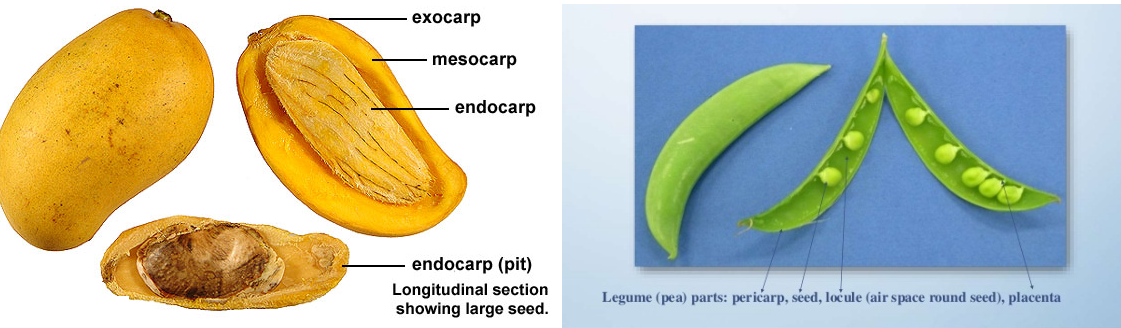
- During the development, ovary becomes fruit, and the ovary wall becomes the fruit wall, known as pericarp. The pericarp has three layers – outer epicarp, middle mesocarp and an inner endocarp.
Classification of Fruits
Fruits are generally classified into three, based on their origin, and development.
Simple fruits
- It is the fruit developed from a single flower having either one (monocarpellary) or numerous (multicarpellary) carpels in a syncrpous condition.
- They can be dry fruits (e.g. Pisum) or fleshy fruits (e.g. Mangifera indica).
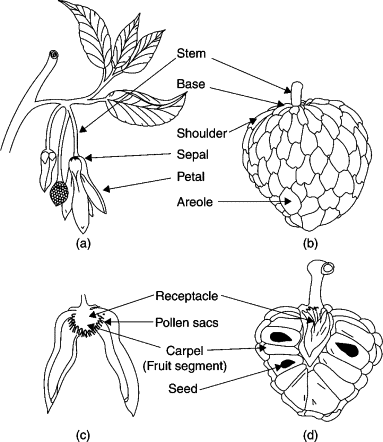
Aggregate fruits
- An aggregate fruit is developed from an apocarpous pistil (carpels – free).
- Each carpel develops into a fruitlet (e.g. Polyalthia).

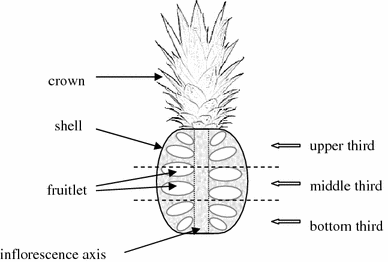
Multiple fruits
- Fruits developed from an inflorescence are termed as a multiple fruit.
- It is also called a composite fruit or sorosis.
- E.g. Pinapple, Jackfruit.