- Frogs have a well-developed and closed type circulatory system (including a blood vascular system and a lymphatic system).
- The lymphatic system consists of – lymph, lymph channels and lymph nodes.
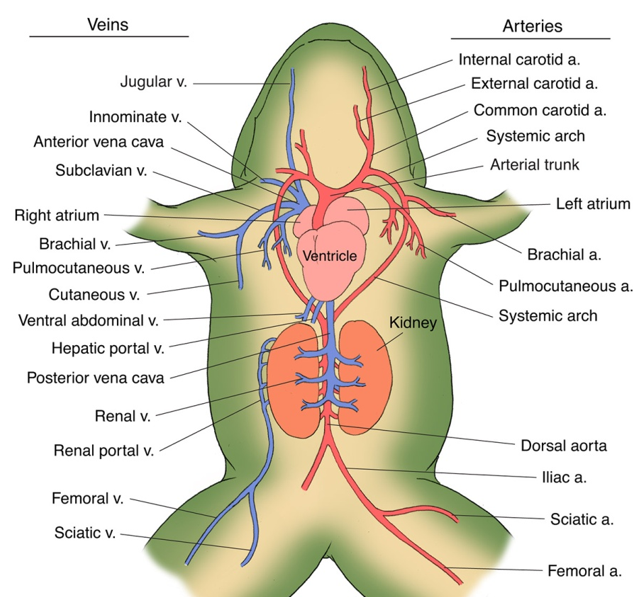
- Blood vascular system: It involves heart, blood vessels and blood
Blood Vessels
-
- The arteries carry blood from the heart to all parts of the body (arterial system).
- The veins collect blood from different parts of body to the heart and form the venous system.
- Special venous connections are present between liver and intestine. It is called hepatic-portal system.
- The venous connections between kidney and lower parts of the body are called renal portal system.
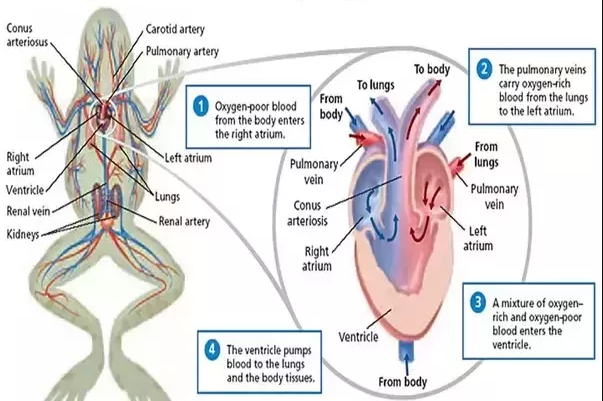
Heart
-
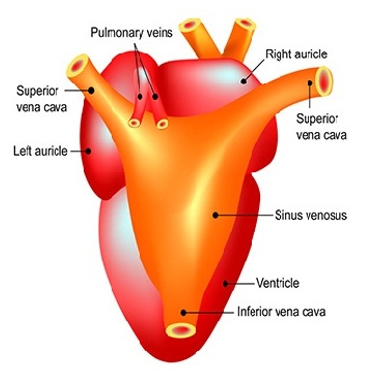
- Amphibian heart is a tripartite (3 chambers) muscular structure situated in the upper part of the body cavity.
-
- It contains two atria and a single ventricle.
- The heart is covered by a membrane called pericardium.
- A triangular structure called sinus venosus is present near the right atrium.
- The flow of venous blood into atrium takes place by the contraction of sinus venosus.
- It receives blood through the major veins called vena cava.
- The ventricle opens into a sac-like conus arteriosus on the ventral side of the heart.
Blood
-
- The blood is composed of plasma and cells.
- The blood cells are RBC (red blood cells) or erythrocytes, WBC (white blood cells) or leucocytes and platelets.
- RBC’s are nucleated and contain red colored pigment namely hemoglobin.
- The lymph is different from blood.
- It lacks few proteins and RBCs.
- The blood carries nutrients, gases and water to the respective sites during the circulation.
- The circulation of blood is achieved by the pumping action of the muscular heart.
Frog: Excretory System
- The excretory product of an adult frog is urea and that of a tadpole is ammonia.
- Excretory wastes are carried by blood into the kidney where it is separated and excreted.
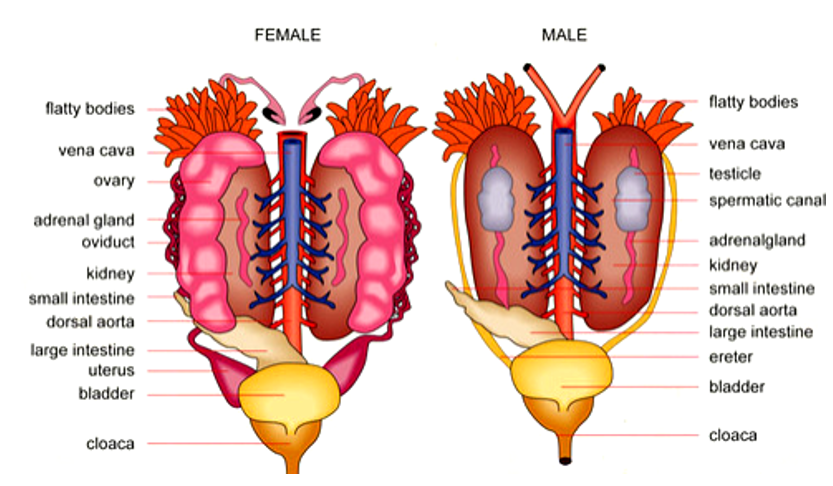
- The excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, ureters, cloaca and urinary bladder.
Kidney
- Kidneys are bean – shaped structures present on either sides of the vertebral column.
- Each kidney is composed of several structural and functional units called uriniferous tubules or nephrons.
Ureters
- A pair of ureter arises from the kidney (one from each kidney).
- In males, the ureters act as a common duct for the passage of wastes and sperm. It is hence known as the urinogenital duct which opens into the cloaca.
- In females the ureters and oviduct open seperately in the cloaca.
Urinary bladder
- It is a thin-walled bulb – like structure present near the rectum. Both rectum and urinary bladder opens into the cloaca.
- The frog excretes urea and thus is a ureotelic animal.