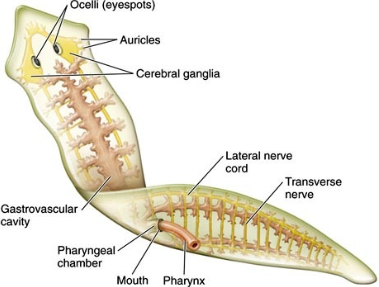
The members of this phylum have dorso-ventrally flattened body and are hence called flatworms. The body has usually ribbon-like or leaf-like appearance.
Habitat: They live as endoparasites inside the body of animals including humans.
Examples:


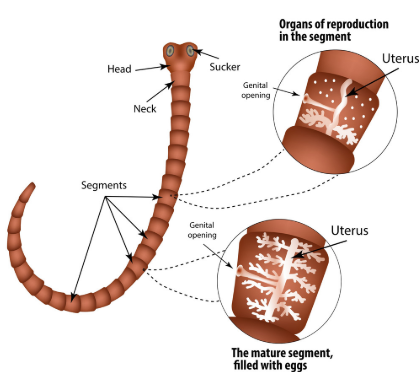
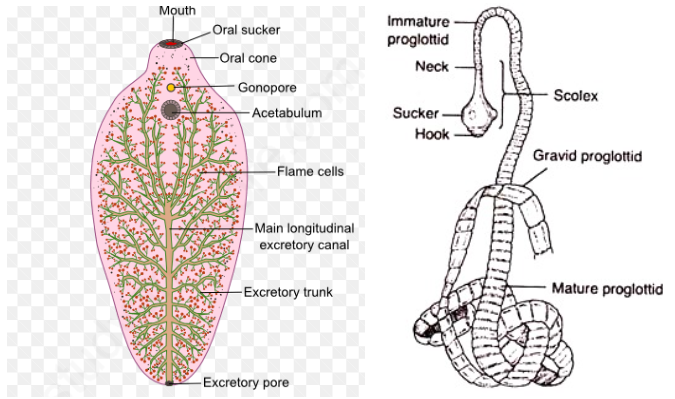
Taenia (Tapeworm) Fasciola (Liver fluke) Planaria.
Body plan: Flatworms are acoelomate animals with blind sac body plan and organ level of organization.
Symmetry: The flatworms are bilateral symmetry.
Germ layer: They are triploblastic organisms.
Body characteristics: Parasitic forms have thick cuticle, suckers and hooks. Free living forms have a ciliated epidermis.
Physiology:
- Respiratory and circulatory systems are absent.
- Excretory cells are called flame cells. These are also involved in osmoregulation.
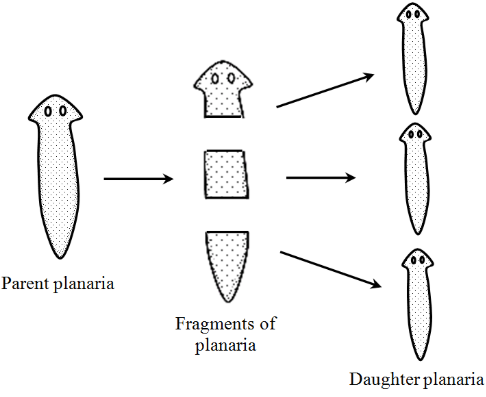
Reproduction: They are hermaphrodites and reproduction occurs by sexual means. But cross- fertilization also occurs frequently. Some members (like Planaria) have great powers for regeneration.
Embryo Development: Fertilization is internal. The development is indirect with many larval stages.
.