The stalk of a flower is called pedicel. A flower with pedicel is called pedicellate flower. Flowers without pedicel are called sessile. The swollen base of the pedicel is called thalamus or receptacle.
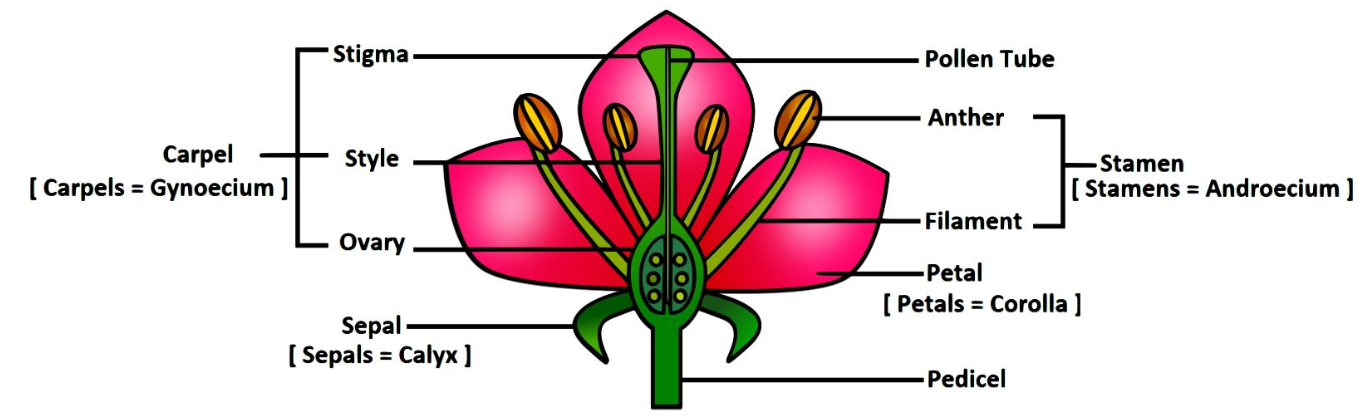
Each flower has four whorls – Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium. A complete flower possesses all the four whorls. If the flower lacks one or more whorls, the flower is called an incomplete flower.
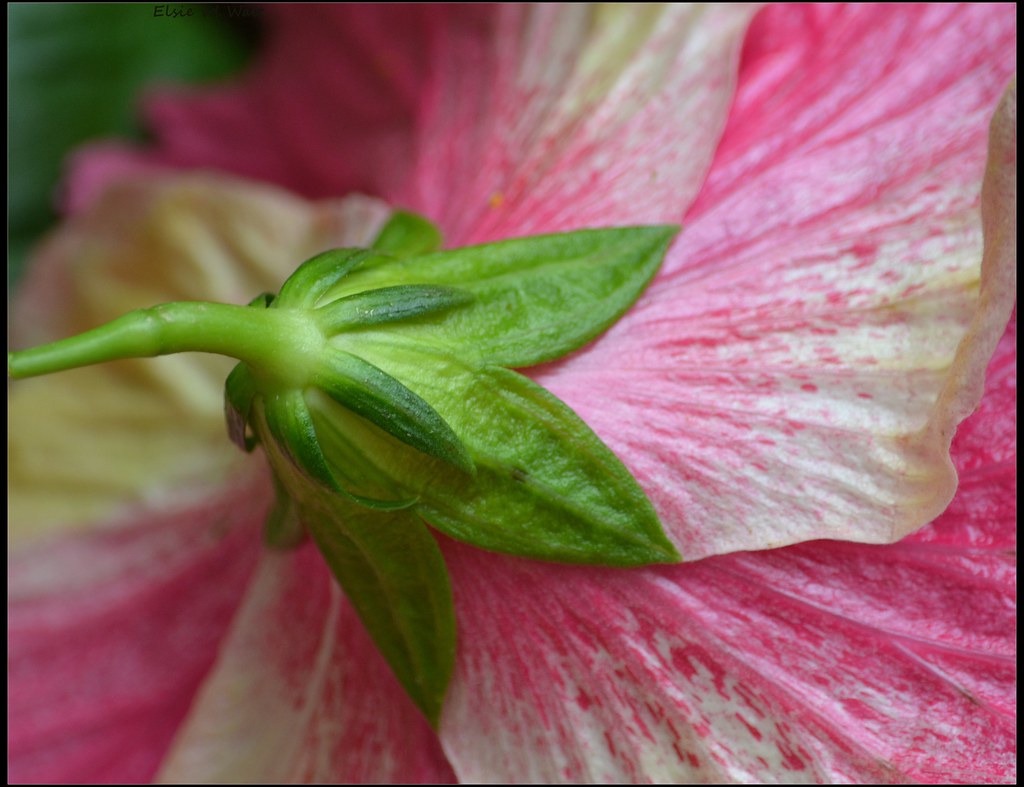
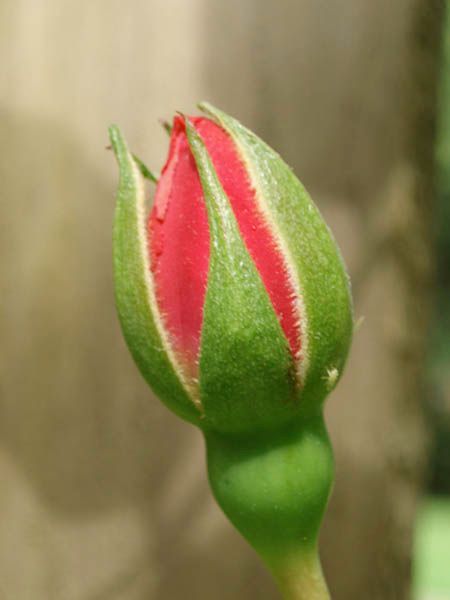



Calyx
- Calyx is the outermost whorl. It is composed of a number of lobes called sepals.
- If the sepals are free, the calyx is called polysepalous.
- If the sepals are fused, it is called, gamosepalous.
- Sepals are usually green in color, and they protect the floral parts of a flower at its bud stage.
Corrolla
- It is the second whorl, and is composed of petals.
- They are usually large, brightly colored and have a strong fragrance inorder to attract insects for pollination.
- When the petals are free, the corolla is called polypetalous.
- If they are fused, it is called gamopetalous.
- Petals may be tubular, bell-shaped, funnel-shaped or wheel-shaped in different flowers.
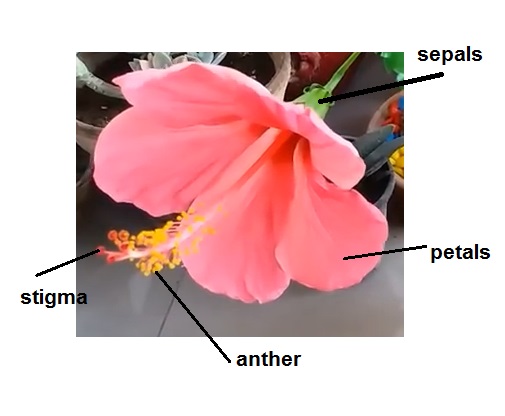
If both calyx and corolla are present in a flower, it is called a dichlamydeous flower. If only one of the above whorls is present, it is called a monochlamydeous flower. If both these whorls are absent, it is called an achlamydeous flower.
Perianth
In some plants, the calyx and corolla are fused, and are not distinguishable from one another. This structure is called a perianth. The separate lobes of a perianth are called tepals.


Aestivation:
The arrangement of floral parts (sepals and petals) in a flower bud is termed as aestivation. There are different types of aestivation.
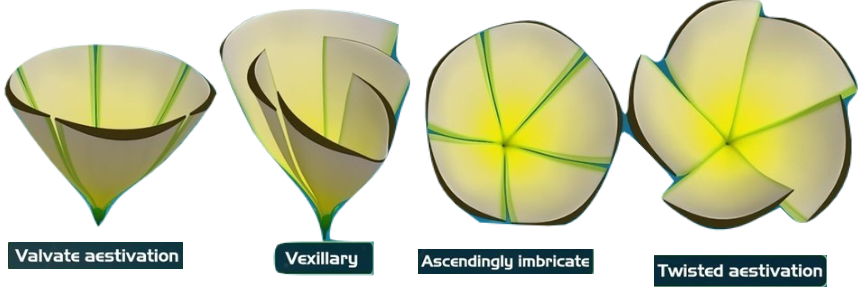
Valvate: The sepals/petals just touch one another at the edges, without overlapping. (e.g. Custard, Apple)
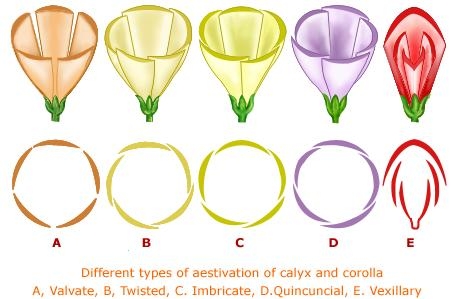
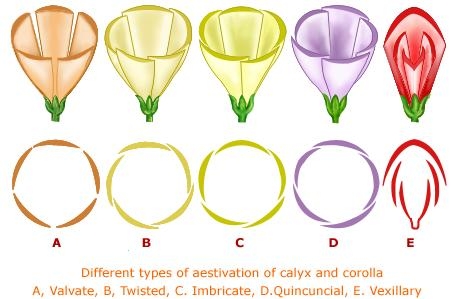
- Twisted: One margin of the whorl overlaps that of the next one, and the other margin is overlapped by another one. (e.g. Hibiscus)
- Imbricate: There is no particular direction for the overlapping of the whorls. One of the five sepals will be internal, one is external, and the other three are partly internal and partly external.
- Quincuncial: Two of the petals would be completely internal; two are completely external, while one is partly internal and partly external.
- Vexillary: One posterior petal would be large and covers two lateral petals. These lateral petals overlap the two anterior and smallest petals. It is also called papilioneceous aestivation.