Organic chemistry – Electronic displacements in a covalent bond
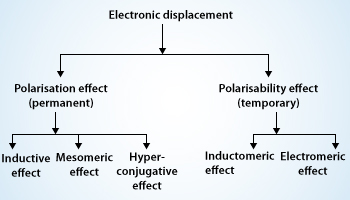
Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are in most of the molecules we encounter either in our clothing, food we eat or even the air we breathe, the water we drink, etc. covalent bonds are the chemical bonds in which electrons are shared by every atom who takes part in the bonding rather than ionic bonds in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another. But it’s not the case that each atom shares the same amount of electrons no, every atom shares different amount of electrons depending on the various things like valance electrons, the another they are making bond with, etc. atoms can actually take more than their fair shares of electrons, even in covalent bonds and that is what leads to the electronic displacements in covalent bond. The electron pairs in these covalent bonds may undergo displacements either of their own or under the influence of other species (atom or group of atoms) or in the presence of an appropriate attacking reagent. The electronic displacements are often responsible for the reactivity of a particular atom and the inertness of others in presence of more active molecules. The main reason for electronic displacements is because of the influence of an atom or a substituent group present in the molecule which causes permanent polarization of the covalent bond. The attacking reagent which influences on covalent bond always bears either a positive or a negative charge. For the successful reaction to occur in a covalent bond bond should possess opposite charge centers to that of reagent molecule. We normally observe that the substrate molecule is usually an electrically neutral molecule. It should develop some polarity on its carbon atom or any substituent atom bonded together and this is what made possible by the electronic displacement. Electronic displacements occur in the molecules because of certain effects they may be permanent or temporary effects. As we above discussed the permanent polarization of the molecules which is because the substituent are permanently operating in the molecules and the other type of effects temporary effects they are brought into play by any attacking reagent. As we remove the attacking regaent the electronic displacement disappears. Four types of electronic displacements are generally noticed in the mechanism of organic reactions. These are given below:
- Inductive effect
- Electromeric effect
- Resonance or mesomeric effect
- Hyperconjugation
From the listed above effects inductive, resonance and hyperconjugation are permanent or polarization effects, while electromeric is a temporary effect. Temporary effect is also known as polarisability effect. Let me tell you a bit about each one of them.
- Inductive effect: The process of displacement of σ-electrons along the saturated carbon chain due to the presence of a polar covalent bond at one end of the chain is called the inductive effect.
- Electromeric effect: The movement of electrons from one atom to another in a multiple bonds at the demand of attacking reagent is called the electromeric effect.
- Hyperconjugation: The interaction between the electrons of π systems and the adjacent σ bonds of the substituent groups in an organic compound is called hyperconjugation.