A carbonyl group is present in the aldehydes and ketones. Mainly, aldehydes are considered as the most important functional groups and often they are called as methanoyl or formyl groups. The name aldehyde is derived from the dehydration of the alcohols. Carbonyl group in the aldehyde is bonded to at least one of the hydrogen atom and in the ketones, the carbonyl group is bonded to the two carbon atoms. Both ketones and aldehydes are the organic compounds that incorporate their carbonyl functional groups. There are two remaining bonds of the carbon atom which may be occupied by the aryl or alkyl substituents or by the hydrogen. The compound is aldehyde if one of the substituents is hydrogen.
Naming Aldehydes
According to the IUPAC system of the nomenclature, a characteristic suffix –al is assigned to the aldehydes. There is a condition for the aldehyde carbonyl group that it must be attached at the end of the carbon chain, so location wise it is given the first position in the numbering and there is no necessity to must include it in the name.
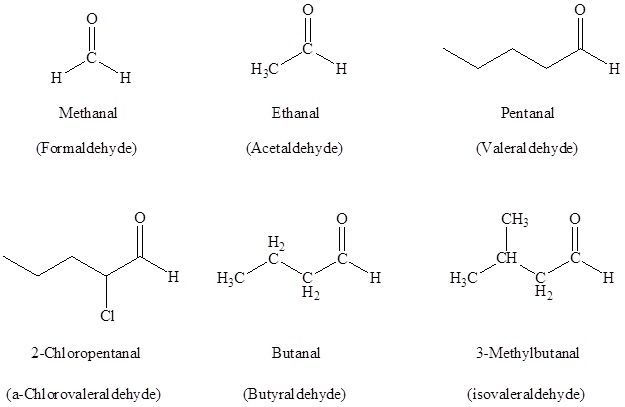
For naming the aldehydes a common method is also used in which the aldehydes which have the common parent chain name similar to those which are used for the carboxylic acids are used as a suffix is added to the end that is the aldehyde. If a common method is used for naming the aldehydes then the carbon atom which is nearest to the carbonyl group is designated by the Greek letters. The atom which is adjacent to the carbonyl function is regarded as alpha, the next that is removed is beta and so on.
Naming Ketones
According to the IUPAC system of nomenclature, a characteristic suffix –one is assigned to the ketones. According to this system, the ketone functional group can be located anywhere within the ring or chain and a location number is used to indicate its position. Normally, the chain numbering is started from the end which is nearest to the carbonyl group.
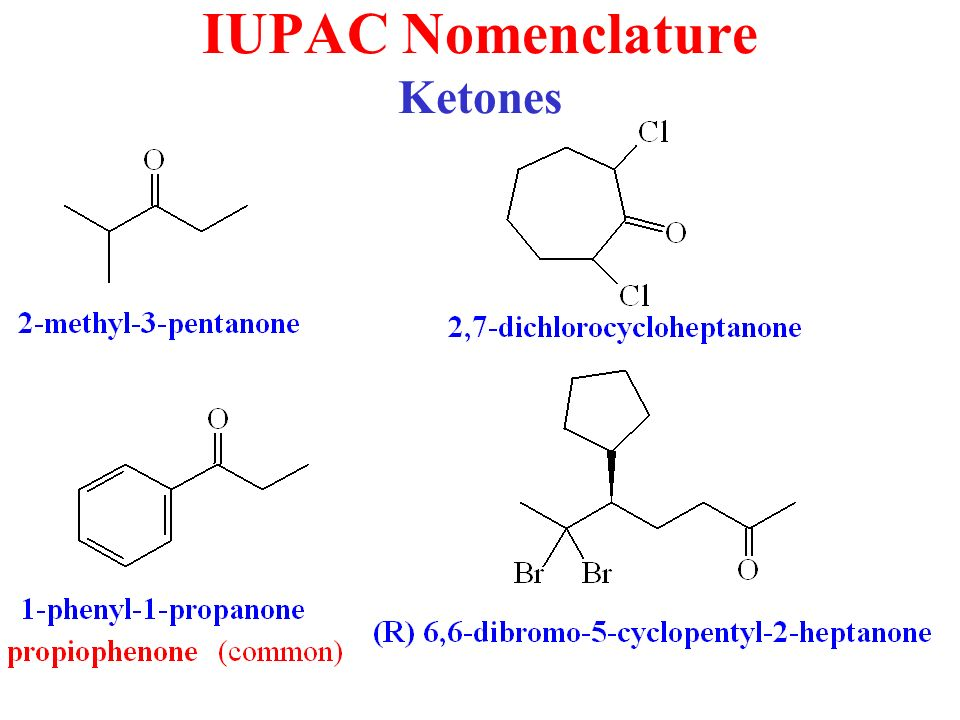
A location number is not required for the simple ketones such as for the propanone and phenylethanone, because for a ketone carbonyl function there is only one possible site. The alkyl groups which are attached are generally arranged according to the alphabetical order. The name of the ketones is given from the parent alkane chain and some of the common ketones are also known by their generic names.