Halogens are more electronegative as compared to carbon. Because of this halogen atoms have a greater tendency than carbon atoms to attract electron density. This makes the very nature of C-X bonds between halogen and carbon polar in nature; the carbon atom bears a partial positive charge whereas the halogen atom bears a partial negative charge.
Nature Of C-X Bond
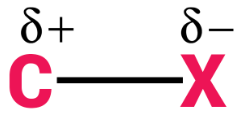
The symbol X is used to denote any general halogen. So, C-X bond basically denotes the bond between carbon and halogen. Halogens are group 17 elements of the modern periodic table. For completing their nearest noble gas configuration, they are short of one electron. The 17th group elements, in increasing order of their atomic sizes, are arranged in the modern periodic table as follows:
- Fluorine
- Chlorine
- Bromine
- Iodine
Carbon is in 14th group and as we know that the electronegativity of elements decreases across a period in the modern periodic table, hence halogens are more electronegative than carbon. This characteristic of halogens as compared to carbon can be attributed to the small size of halogen atoms. As it can be seen that the size of halogen atom increases as we go down the group in the periodic table, fluorine atom is the smallest and iodine atom, the largest. Consequently from C—F to C—I, the carbon-halogen bond length also increases.
Features of C-X bonds
The various features of a C-X bond are as follows:
- Since halogens are more electronegative than carbon, the carbon-halogen bond is polarized. Due to high electronegativity of halogens, they attract the shared pair of electrons more towards themselves and thus halogens gain a slight negative charge and carbon gets a slight positive charge.
- Only single bonds are formed between one carbon and one halogen atom as halogens need only 1 electron to complete their nearest noble gas configuration, while carbon needs 4 electrons to complete its nearest noble gas configuration. Hence after the bond formation between C and X, halogen atom completes its octet but carbon still needs 3 more electrons to complete its octet.
- With increase in the size of halogens from fluorine to astatine, the C-X bond length increases and also the bond dissociation strength decreases.
- We know that electronegativity decreases down the group, hence dipole moment which depends on the difference in electronegativity of carbon and halogen also decreases down the group. The only exception in group 17 is that the dipole moment of the C-Cl bond is more than C-F; everything else follows the normal trend.